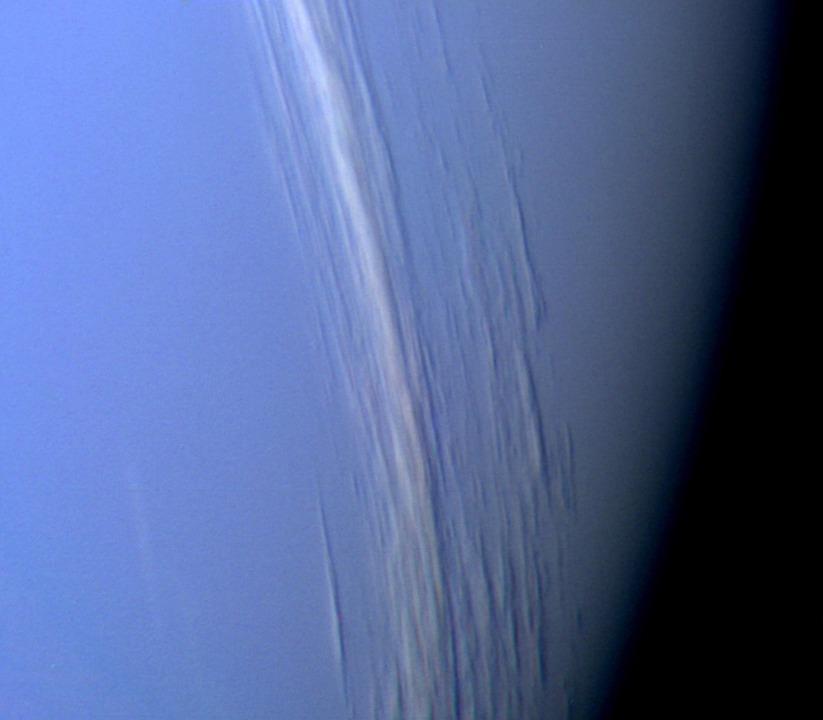
So far, space agencies all over the world have closely explored up until Saturn, keeping tabs on the activity seen on these planets and their respective sets of moons. Recently, NASA announced another upcoming mission, this time going all the way to Neptune.
NASA announced its Trident mission, which will explore Neptune and its moon, Triton. The mission is named as such after the agency’s “three-pronged” objectives to study its magnetic field. NASA also plans to map the entire surface of Triton to study its plume activity and behavior. Triton orbits in the direction against Neptune.
The agency will be choosing two concept studies in the summer of 2021 with an expected launch date to take place in 2025. Exploring Trident could potentially solve the mystery of what triggers the plumes following a previous mission done by NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft to Triton 30 years prior. The spacecraft revealed icy plumes coming from Triton’s surface.
Time will tell when information about these plumes would be made available as Trident is not expected to reach Triton until 2038, making it a 13-year journey to Neptune’s moon. Many experts were baffled at how a moon like Triton would remain active despite being so far away from the Sun.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory Scientist Karl Mitchell said, “We know the surface has all these features that we’ve never seen before, which motivates us to want to know ‘How does this world work?’”
Previously, scientists discovered the volcano-like structures on another planet’s moon. Astronomers found these volcano-like structures on the polar regions of Saturn’s moon Titan and they believe these could be the cause of eruptions that may still be happening today. According to the study which made use of the data from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, the link between the volcanic craters and polar lakes is in line with the moon having a volcanic origin through these eruptions.
Because some craters appear to be freshly made, this suggests that volcanic activity may be present and ongoing on Titan. The agency’s Cassini spacecraft revealed that there are land formations on Titan that are similar to Earth, such as sand dunes, river valleys, and lakes, also suggesting internal heat in Titan.



 Neuralink Plans High-Volume Brain Implant Production and Fully Automated Surgery by 2026
Neuralink Plans High-Volume Brain Implant Production and Fully Automated Surgery by 2026  Senate Sets December 8 Vote on Trump’s NASA Nominee Jared Isaacman
Senate Sets December 8 Vote on Trump’s NASA Nominee Jared Isaacman  Trump and Merck KGaA Partner to Slash IVF Drug Costs and Expand Fertility Coverage
Trump and Merck KGaA Partner to Slash IVF Drug Costs and Expand Fertility Coverage  Tabletop particle accelerator could transform medicine and materials science
Tabletop particle accelerator could transform medicine and materials science  Lost in space: MethaneSat failed just as NZ was to take over mission control – here’s what we need to know now
Lost in space: MethaneSat failed just as NZ was to take over mission control – here’s what we need to know now  SpaceX Starship Explodes in Texas During Test, Citing Nitrogen Tank Failure
SpaceX Starship Explodes in Texas During Test, Citing Nitrogen Tank Failure  FDA Pilot Program Eases Rules for Nicotine Pouch Makers
FDA Pilot Program Eases Rules for Nicotine Pouch Makers  SpaceX’s Starship Completes 11th Test Flight, Paving Way for Moon and Mars Missions
SpaceX’s Starship Completes 11th Test Flight, Paving Way for Moon and Mars Missions  CDC Vaccine Review Sparks Controversy Over Thimerosal Study Citation
CDC Vaccine Review Sparks Controversy Over Thimerosal Study Citation  Is space worth the cost? Accounting experts say its value can’t be found in spreadsheets
Is space worth the cost? Accounting experts say its value can’t be found in spreadsheets  NASA Astronauts Wilmore and Williams Recover After Boeing Starliner Delay
NASA Astronauts Wilmore and Williams Recover After Boeing Starliner Delay