Any currency option deal may be equivalently valued as either a call or a put using a parity condition that is specific to currency options. We may see that when put-call parity is broken, risk-free arbitrage opportunities may exist.
We’ve considered AUDNZD ATM contracts to exhibit the concept, this condition states that:
Holding a call option to buy 1 unit of NZD for x units of AUD is equal to the holding a put option to sell x units of AUD for 1/x units of NZD.
Let’s suppose a foreign trader has purchased NZD ATM Call / AUD ATM Put of 1Y expiry in European vanilla style with a face value of AUD $1 million.
The risk-free rate in AUS is +2.012% (3M prevailing AUS T-bill rate),
The risk-free rate in NZ is 2.070% (3M prevailing NZ T-bill rate),
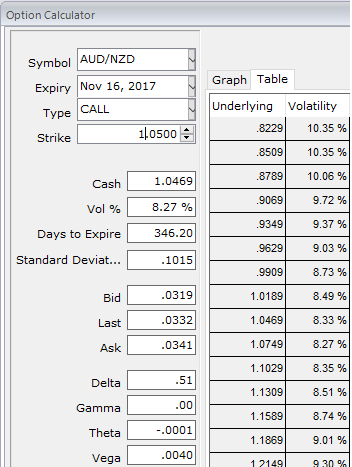
FX rate volatility is at around 8.27%, and let’s say option expiry would be 1 year.
The spot FX is 1.0469 (Direct quote while articulating) and the strike rate is 1.05 since this is 1y ATM contract.
Consider AUD as the domestic CCY, so the spot must be quoted as the number of units of NZD required to purchase 1AUD.
To value the option as a call, we treat the AUD as the domestic CCY and the NZD as the foreign CCY. The domestic and foreign interest rates are therefore 2.012% and 2.070%, respectively.
Note that once both the spot and strike quotes are converted, the call option is out of the money.
When these parameters are passed to the Garman-Kohlhagen routine, a value of NZD 0.03573 is returned.
This is a per unit value, and since a total of 1 million Aussie dollars underlie the deal, the total premium value is 0.03573 * 1,000,000 = NZD 35,730 (with allowance for rounding).
In order to demonstrate the parity condition, we could also value this deal as a put. In this case, the domestic (foreign) CCY is the AUD (NZD), the domestic (foreign) interest rate is 2.070, the spot rate is 1.0469 and the strike rate is 1.05.
With these inputs, the model returns a value per unit FX of AUD 0.320 and the total value of the premium on the deal is AUD 32,000. This amount is equivalent to the NZD premium computed above when it is converted to NZD at the spot rate of 1.0469.
If the spot FX is expressed in a consistent approach to the strike price, then the computed total premium for the call leg will be the same as the computed total premium for the put leg, assuming both values are expressed in the same currency.



 S&P 500 Relies on Tech for Growth in Q4 2024, Says Barclays
S&P 500 Relies on Tech for Growth in Q4 2024, Says Barclays  Lithium Market Poised for Recovery Amid Supply Cuts and Rising Demand
Lithium Market Poised for Recovery Amid Supply Cuts and Rising Demand  Stock Futures Dip as Investors Await Key Payrolls Data
Stock Futures Dip as Investors Await Key Payrolls Data  Geopolitical Shocks That Could Reshape Financial Markets in 2025
Geopolitical Shocks That Could Reshape Financial Markets in 2025  Moody's Upgrades Argentina's Credit Rating Amid Economic Reforms
Moody's Upgrades Argentina's Credit Rating Amid Economic Reforms  Mexico's Undervalued Equity Market Offers Long-Term Investment Potential
Mexico's Undervalued Equity Market Offers Long-Term Investment Potential  2025 Market Outlook: Key January Events to Watch
2025 Market Outlook: Key January Events to Watch  Oil Prices Dip Slightly Amid Focus on Russian Sanctions and U.S. Inflation Data
Oil Prices Dip Slightly Amid Focus on Russian Sanctions and U.S. Inflation Data  U.S. Treasury Yields Expected to Decline Amid Cooling Economic Pressures
U.S. Treasury Yields Expected to Decline Amid Cooling Economic Pressures  Global Markets React to Strong U.S. Jobs Data and Rising Yields
Global Markets React to Strong U.S. Jobs Data and Rising Yields  China's Refining Industry Faces Major Shakeup Amid Challenges
China's Refining Industry Faces Major Shakeup Amid Challenges  UBS Predicts Potential Fed Rate Cut Amid Strong US Economic Data
UBS Predicts Potential Fed Rate Cut Amid Strong US Economic Data  Bank of America Posts Strong Q4 2024 Results, Shares Rise
Bank of America Posts Strong Q4 2024 Results, Shares Rise  Moldova Criticizes Russia Amid Transdniestria Energy Crisis
Moldova Criticizes Russia Amid Transdniestria Energy Crisis  Trump’s "Shock and Awe" Agenda: Executive Orders from Day One
Trump’s "Shock and Awe" Agenda: Executive Orders from Day One  China’s Growth Faces Structural Challenges Amid Doubts Over Data
China’s Growth Faces Structural Challenges Amid Doubts Over Data  Energy Sector Outlook 2025: AI's Role and Market Dynamics
Energy Sector Outlook 2025: AI's Role and Market Dynamics