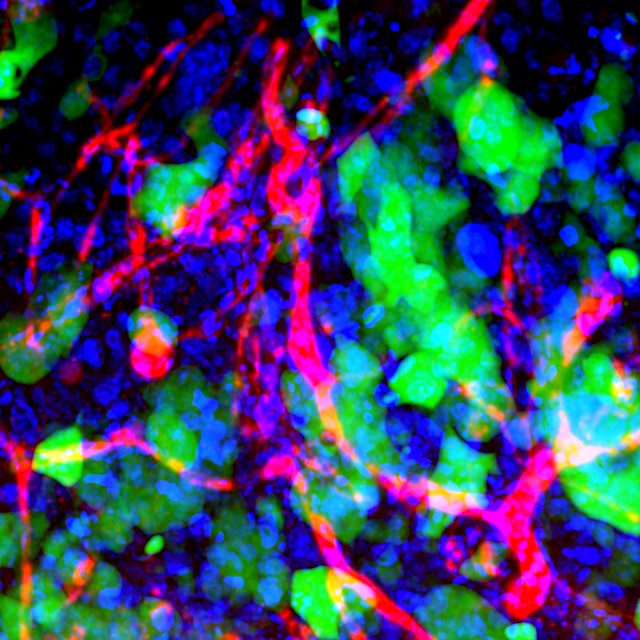
Scientists around the world have various strategies finding the potential cancer cure or come up with a much better treatment regimen to help patients live longer. Researchers from Wisconsin and Texas recently published a study focused on the possible benefits from a primitive fish in advancing brain cancer and stroke treatments.
Researchers from the University of Wisconsin-Madison and The University of Texas at Austin are focusing on the benefits of using lampreys in delivering therapeutic drugs to the brain that could specifically target cancer cells. The Britannica Encyclopedia refers to lampreys as a “primitive” fish characterized by having no jaw and commonly found in fresh and coastal waters.
The study, published on Science Advances last week, explains that the brain has a natural wall called blood-brain barrier (BBB) to avoid disease-carrying agents from entering it. However, physical trauma, stroke, cancer tumors, and other conditions could disrupt the BBB. This could then be exploited to target specific regions and effectively deliver therapeutic drugs to cure or treat certain diseases and conditions.
Meanwhile, the disrupted areas of BBB varies in each condition, but the constant factor in these cases is the exposure of the brain extracellular matrix. In general, ECM is referred to as a “scaffolding” and a macromolecular network known to be responsible for cell-to-cell communication. Researchers believe that the ECM could be used for delivering drugs to specific areas of the brain through a disrupted BBB.
“To test the potential benefits of ECM-targeted drug delivery, we first applied the concept to the incurable brain cancer, glioblastoma (GBM),” the scientists explain. “Better GBM therapies are sorely needed because patients have a uniformly poor prognosis with a median survival of fewer than 2 years despite aggressive clinical treatments of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.” This leads to the hypothesis that such a method has the potential to become an effective treatment for complicated conditions such as brain cancer.
For this specific experiment, the researchers specifically chose an antigen found on lampreys called variable lymphocyte receptors. “ VLRs could possibly recognize conserved proteins and glycans in ECM that may not be effectively targeted by mammalian antibodies,” the study explains.
However, the study has more tests to go through. Medical News Today reports that the researchers are currently set to experiment how this process would perform in other conditions that affect other parts of the human body.



 Astronomers have discovered another puzzling interstellar object − this third one is big, bright and fast
Astronomers have discovered another puzzling interstellar object − this third one is big, bright and fast  NASA Astronauts Wilmore and Williams Recover After Boeing Starliner Delay
NASA Astronauts Wilmore and Williams Recover After Boeing Starliner Delay  Lost in space: MethaneSat failed just as NZ was to take over mission control – here’s what we need to know now
Lost in space: MethaneSat failed just as NZ was to take over mission control – here’s what we need to know now  Trump Signs Executive Order to Boost AI Research in Childhood Cancer
Trump Signs Executive Order to Boost AI Research in Childhood Cancer  Neuralink Expands Brain Implant Trials with 12 Global Patients
Neuralink Expands Brain Implant Trials with 12 Global Patients  SpaceX Starship Test Flight Reaches New Heights but Ends in Setback
SpaceX Starship Test Flight Reaches New Heights but Ends in Setback  Trump and Merck KGaA Partner to Slash IVF Drug Costs and Expand Fertility Coverage
Trump and Merck KGaA Partner to Slash IVF Drug Costs and Expand Fertility Coverage  Blue Origin’s New Glenn Achieves Breakthrough Success With First NASA Mission
Blue Origin’s New Glenn Achieves Breakthrough Success With First NASA Mission  FDA Pilot Program Eases Rules for Nicotine Pouch Makers
FDA Pilot Program Eases Rules for Nicotine Pouch Makers  SpaceX Prioritizes Moon Mission Before Mars as Starship Development Accelerates
SpaceX Prioritizes Moon Mission Before Mars as Starship Development Accelerates  Senate Sets December 8 Vote on Trump’s NASA Nominee Jared Isaacman
Senate Sets December 8 Vote on Trump’s NASA Nominee Jared Isaacman  Cogent Biosciences Soars 120% on Breakthrough Phase 3 Results for Bezuclastinib in GIST Treatment
Cogent Biosciences Soars 120% on Breakthrough Phase 3 Results for Bezuclastinib in GIST Treatment