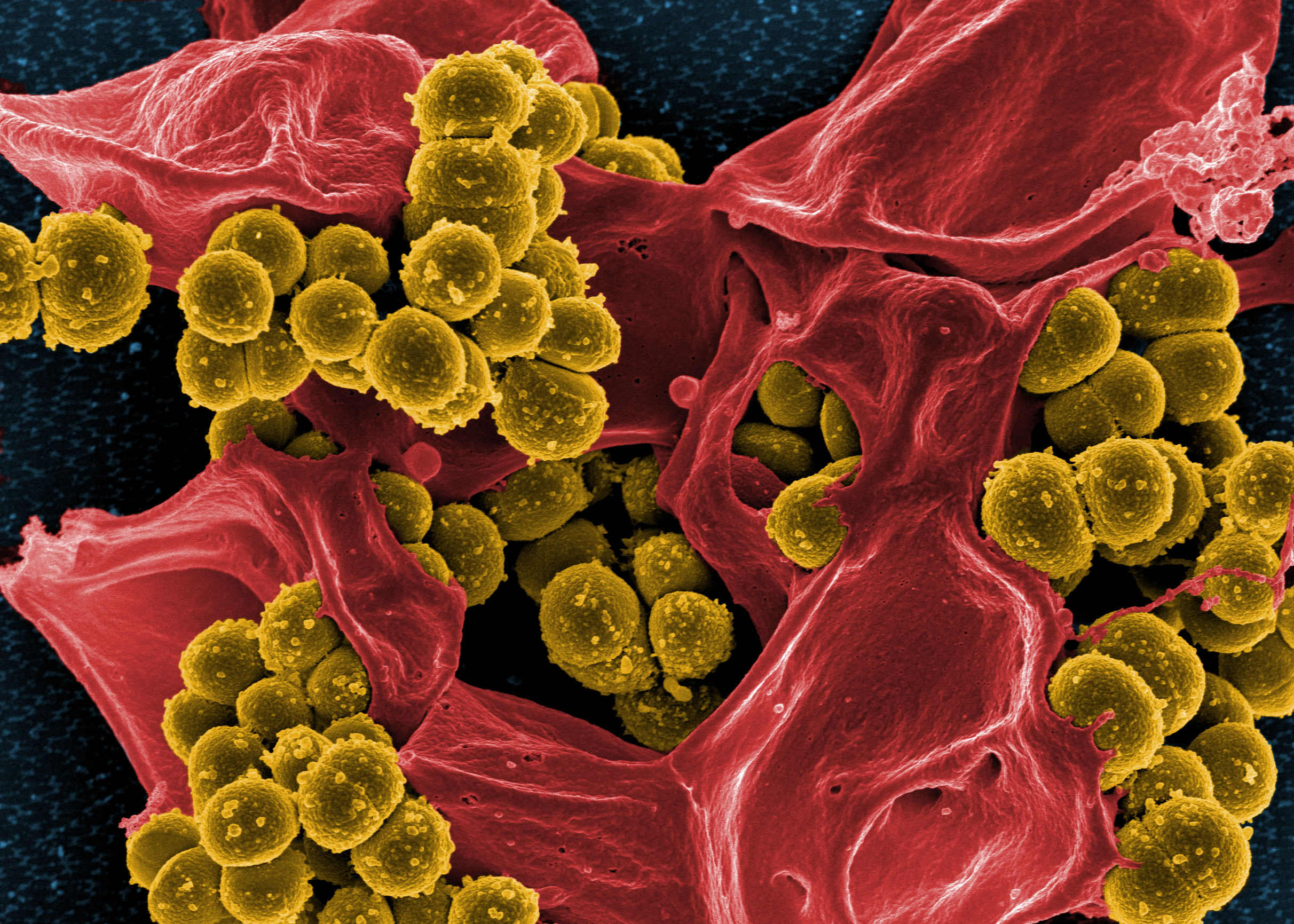
Elon Musk’s rocket company SpaceX is slated to send a rocket up into space on February 14th carrying a very special payload. With the alarming rate of growth of drug-resistant superbugs on Earth, scientists now want to send an example called Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) into space for study.
Anyone who knows anything of MRSA will likely have felt chills running down their spine at the very thought of being in an enclosed space with the microorganism in Zero-gravity. However, this is exactly what scientists are planning on doing with the purpose of studying the super bacteria, Futurism reports.
Studying MRSA in space has several advantages compared to when studying it here on Earth, the biggest of which is to accelerate the mutation of the bacteria. Without the constant pressure exerted by the planet’s gravity, MRSA will basically be able to change at an accelerated rate, which ties directly into its ability to infect and even kill its hosts.
Normally associated with symptoms like red, swollen bumps on the skin, MRSA is an incredibly efficient killer. The only way to stop it is to develop a method of counteracting its effects in a specific manner, which will need first-hand observation of how it develops in the first place.
Once it reaches space, Dr. Anita Goel and her team of scientists will be handling the deadly bacteria, Yahoo reports. Dr. Goel won the Galactic Grant Competition back in 2015, which allowed her to receive $500,000 in grant money. At the event, she outlines her plans for the future, including a trip to the International Space Station to accelerate the finding of cures to deadly organisms.
"We will leverage the microgravity environment on the ISS to accelerate the Precision Medicine revolution here on Earth," Dr. Goel explained. "Our ability to anticipate drug-resistant mutations with Gene-RADAR will lead to next-generation antibiotics that are more precisely tailored to stop the spread of the world's most dangerous pathogens."



 Trump Signs Executive Order to Boost AI Research in Childhood Cancer
Trump Signs Executive Order to Boost AI Research in Childhood Cancer  Trump and Merck KGaA Partner to Slash IVF Drug Costs and Expand Fertility Coverage
Trump and Merck KGaA Partner to Slash IVF Drug Costs and Expand Fertility Coverage  Astronomers have discovered another puzzling interstellar object − this third one is big, bright and fast
Astronomers have discovered another puzzling interstellar object − this third one is big, bright and fast  Neuralink Expands Brain Implant Trials with 12 Global Patients
Neuralink Expands Brain Implant Trials with 12 Global Patients  Neuren Pharmaceuticals Surges on U.S. Patent Win for Rare Disorder Drug
Neuren Pharmaceuticals Surges on U.S. Patent Win for Rare Disorder Drug  CDC Vaccine Review Sparks Controversy Over Thimerosal Study Citation
CDC Vaccine Review Sparks Controversy Over Thimerosal Study Citation  Eli Lilly’s Inluriyo Gains FDA Approval for Advanced Breast Cancer Treatment
Eli Lilly’s Inluriyo Gains FDA Approval for Advanced Breast Cancer Treatment  FDA Adds Fatal Risk Warning to J&J and Legend Biotech’s Carvykti Cancer Therapy
FDA Adds Fatal Risk Warning to J&J and Legend Biotech’s Carvykti Cancer Therapy  SpaceX’s Starship Completes 11th Test Flight, Paving Way for Moon and Mars Missions
SpaceX’s Starship Completes 11th Test Flight, Paving Way for Moon and Mars Missions  Cogent Biosciences Soars 120% on Breakthrough Phase 3 Results for Bezuclastinib in GIST Treatment
Cogent Biosciences Soars 120% on Breakthrough Phase 3 Results for Bezuclastinib in GIST Treatment  SpaceX Starship Test Flight Reaches New Heights but Ends in Setback
SpaceX Starship Test Flight Reaches New Heights but Ends in Setback  Tabletop particle accelerator could transform medicine and materials science
Tabletop particle accelerator could transform medicine and materials science  NASA and Roscosmos Chiefs Meet in Florida to Discuss Moon and ISS Cooperation
NASA and Roscosmos Chiefs Meet in Florida to Discuss Moon and ISS Cooperation  Lost in space: MethaneSat failed just as NZ was to take over mission control – here’s what we need to know now
Lost in space: MethaneSat failed just as NZ was to take over mission control – here’s what we need to know now