This week provided a first tiny glimpse into the labour-market fallout from Australia’s recent lockdowns.
Australian Bureau of Statistics published the wage price index for the June quarter yesterday, showing sluggish wages growth, below forecasts. The labour force figures for July, out today, is an impressive 4.6%, but tempered by the number of people who have stopped looking for work and a higher underemployment rate.
These numbers tell us how the labour market is recovering from last year’s massive pandemic hit. It’s also a sneak peak into how it might be affected by the current lockdowns.
The Greater Sydney lockdown officially began on June 26 – right at the end of the June quarter (the virus had been circulating in Sydney since mid June). So the June quarter figures give us a baseline for the labour market before the big hit from what looks like several months of lockdowns in Sydney, NSW and maybe beyond. We also have a glimpse of the first two weeks of the “self-lockdown” in Sydney, where people pull back on economic activity due to the virus circulating.
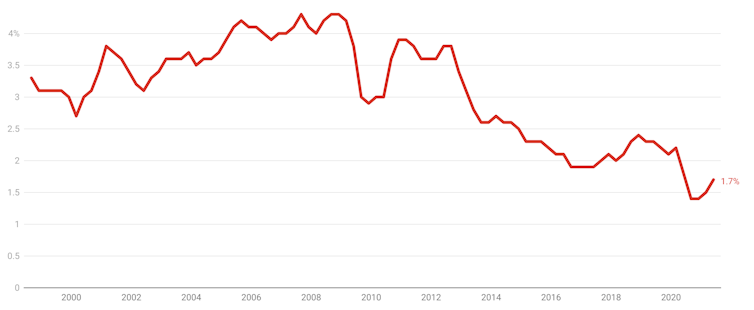
Annual wages growth of 1.7%
The wage price index — measuring wages growth — increased by 0.4% in the June quarter. This was below consensus forecasts of 0.6%, and put the annual rate at 1.7%. This just above the 2020 low of 1.4%.
Wage price index, annual growth
Total hourly rates of pay excluding bonuses, seasonally adjusted. Change from corresponding quarter of previous year. ABS Wage Price Index
All that anecdotal chatter about how it has been impossible to get workers in this industry or that certainly didn’t make its way into the aggregate data.
There were sectoral differences in wage pressures. Three sectors recorded annual increases in wages above 2% — construction (2.2%), professional services (2.5%) and other services (2.6%). The smallest increases were in rental, hiring and real estate services (1.1%), administrative and support services (1.0%) and arts and recreation services (0.9%).
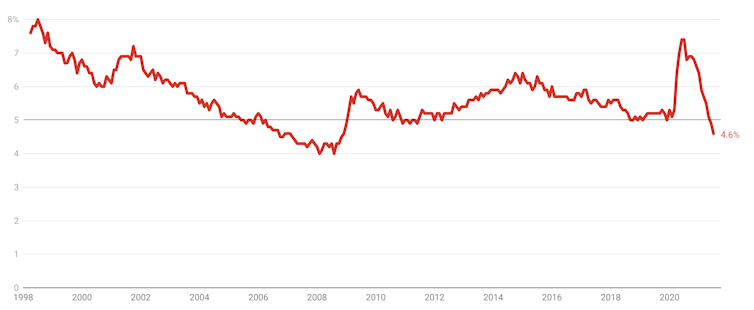
Unemployment rate hits 4.6%
Thursday’s labour force figures came on the back of a stunningly good June rate of 4.9%. July’s rate is stunning again. Kind of.
The monthly unemployment rate dropping to 4.6% represented 39,900 fewer unemployed persons and a slight increase in employed persons, by 2,200 to 13,156,400.
Unemployment rate, seasonally adjusted
Less positive was that the 4.6% rate also reflected a drop in labour force participation, from 66.2% to 66.0%, and that the official underemployment rate jumped from 7.9% to 8.3%.
The fuzzy demarcation between what makes one unemployed versus underemployed as well as the effect of people leaving the labour market is why I always focus in all jobs figures on the “total hours worked”.
This remained effectively steady in July, at 1.778 billion hours.
Overall, therefore, these figures represent very good news. Perhaps the most important implication is that all the naysayers who suggested we could never get unemployment down to or below 4% look — at least so far — wrong.
The immigration illusion
Speaking of folks being wrong, the jobs data also bear on Reserve Bank of Australia governors Philip Lowe’s recent statements about the effect of immigration and wages.
In a speech in early July Lowe suggested high levels of immigration in recent years was an important reason for low wages growth.
Others, including myself, think this view is not supported by the data. Low wages growth since 2013 has a lot more to do with global shifts in technology, the phenomenon of “secular stagnation”, and the fact the Reserve Bank kept interest rates too high, for too long, until finally giving into pressure to cut them in 2019.
The latest data — if looking at the data is your thing — show that, with effectively zero immigration wages, growth remains low. It’s barely moving even in the sectors where immigration is meant to play the biggest role, such as services and construction.
Moreover, even with unemployment falling to 4.6%, there’s relatively little upward pressure. This suggests getting unemployment down to or below 4% not only might be achievable but necessary to get inflation back into the RBA’s target band of 2–3%.
Lockdown impacts still to come
That said, this might be the last good news for a while.
The next quarter’s figures will capture the effect of lockdown for perhaps the entire three months in Greater Sydney, as well as a signifcant amount of time elsewhere. Fiscal support measures such as JobSaver and the Disaster Payment definitely help but they will only stem a flow of bad labour-market numbers.
In the longer term, though, we can and should expect our policy makers — fiscal and monetary — to show us an unemployment number with a 3 in front of it in 2022 or 2023.



 Oil Prices Slip as U.S.-Iran Talks Ease Middle East Tensions
Oil Prices Slip as U.S.-Iran Talks Ease Middle East Tensions  Japan Economy Poised for Q4 2025 Growth as Investment and Consumption Hold Firm
Japan Economy Poised for Q4 2025 Growth as Investment and Consumption Hold Firm  Japanese Pharmaceutical Stocks Slide as TrumpRx.gov Launch Sparks Market Concerns
Japanese Pharmaceutical Stocks Slide as TrumpRx.gov Launch Sparks Market Concerns  Trump Lifts 25% Tariff on Indian Goods in Strategic U.S.–India Trade and Energy Deal
Trump Lifts 25% Tariff on Indian Goods in Strategic U.S.–India Trade and Energy Deal  Australian Household Spending Dips in December as RBA Tightens Policy
Australian Household Spending Dips in December as RBA Tightens Policy  Yen Slides as Japan Election Boosts Fiscal Stimulus Expectations
Yen Slides as Japan Election Boosts Fiscal Stimulus Expectations  Asian Stocks Slip as Tech Rout Deepens, Japan Steadies Ahead of Election
Asian Stocks Slip as Tech Rout Deepens, Japan Steadies Ahead of Election  Vietnam’s Trade Surplus With US Jumps as Exports Surge and China Imports Hit Record
Vietnam’s Trade Surplus With US Jumps as Exports Surge and China Imports Hit Record  UK Starting Salaries See Strongest Growth in 18 Months as Hiring Sentiment Improves
UK Starting Salaries See Strongest Growth in 18 Months as Hiring Sentiment Improves  Gold and Silver Prices Rebound After Volatile Week Triggered by Fed Nomination
Gold and Silver Prices Rebound After Volatile Week Triggered by Fed Nomination  China Extends Gold Buying Streak as Reserves Surge Despite Volatile Prices
China Extends Gold Buying Streak as Reserves Surge Despite Volatile Prices  India–U.S. Interim Trade Pact Cuts Auto Tariffs but Leaves Tesla Out
India–U.S. Interim Trade Pact Cuts Auto Tariffs but Leaves Tesla Out  Asian Currencies Stay Rangebound as Yen Firms on Intervention Talk
Asian Currencies Stay Rangebound as Yen Firms on Intervention Talk  Australian Pension Funds Boost Currency Hedging as Aussie Dollar Strengthens
Australian Pension Funds Boost Currency Hedging as Aussie Dollar Strengthens  Dow Hits 50,000 as U.S. Stocks Stage Strong Rebound Amid AI Volatility
Dow Hits 50,000 as U.S. Stocks Stage Strong Rebound Amid AI Volatility  Asian Markets Surge as Japan Election, Fed Rate Cut Bets, and Tech Rally Lift Global Sentiment
Asian Markets Surge as Japan Election, Fed Rate Cut Bets, and Tech Rally Lift Global Sentiment