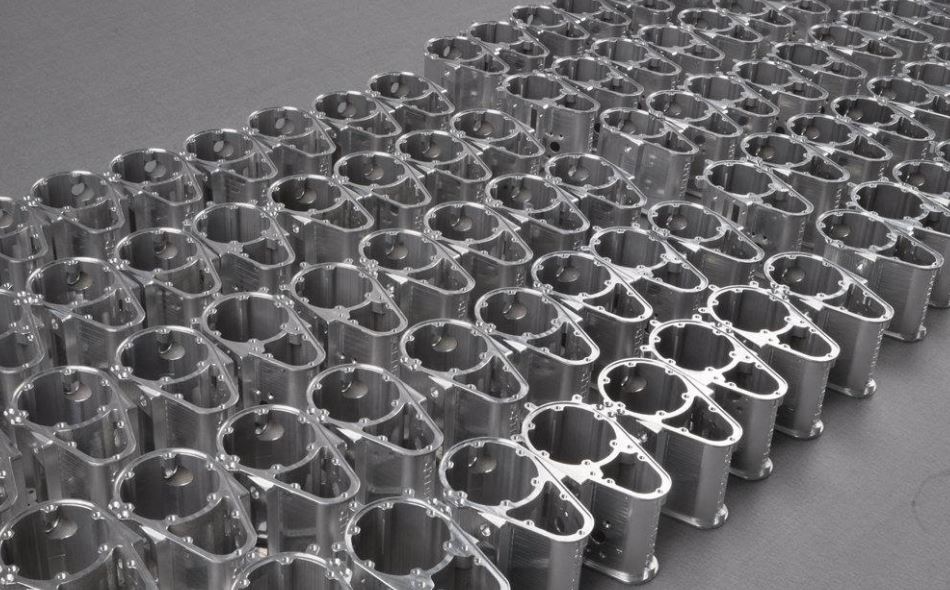
Aluminum plays a significant role in the CNC (computer numerical control) prototyping industry. In actuality, this silvery-white, soft-textured, non-metallic, ductile metal is one of the most commonly used materials in the industry. As a result of its properties, it has tons of applications in several fields, including rail transportation, aerospace engineering, and marine engineering. The central focus on this element is its lightweight and durability. Additionally, its aesthetic and thermal qualities endear this material to the automotive industry. In building prototypes, machinists must cut CNC aluminum to precision. Wayken Hence, many companies implement CNC routing.
These routers are machines that cut and mill aluminum parts to form 3D components. Using this method, manufacturers can curb errors and eliminate material wastage, thereby boosting production output. CNC routers can range from small DIY machines to giant industrial equipment – depending on the needs of the manufacturing plant. Aluminum is one of the easiest metals to cut in the CNC prototyping industry. Couple this feature with its properties, and then it becomes obvious why engineers favor this material. If you want to know more this aspect, you may find more tips for CNC aluminum machining from Wayken.
Aluminum in CNC Prototyping
In CNC aluminum prototyping, CNC shops manufacture aluminum into different forms of alloys. One aluminum alloy that sits at the forefront of the industry is the 6061-T6. Its low density and high tensile strength make it the most sought after in the military, transportation, aerospace, and electronics industries. This aluminum prototyping has a significant tolerance to control – to the point of 0.01MM. On this account, CNC manufacturers can fabricate and rollout high-quality aluminum prototypes with high precision. But how is this done? Most CNC shops use a technique known as CNC milling. This methodology makes it easier to mill high-fidelity aluminum components at high speeds.
The implementation of this CNC technology in several industries has led to the production of CNC-machined aluminum parts, which has, in turn, served the purpose of milling, grinding, and turning. Interestingly, its application to the CNC prototyping industry keeps growing at a steady pace. Some of the end-products of aluminum prototyping include dowel pins, front panels, spline shafts, medical devices, EMI-housings, and lighting fixtures.
Characteristics and Advantages of Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum has a high demand in the CNC prototyping industry due to its properties and advantages. The following contains a list of its attributes:
-
Resilience
When applying static and dynamic loading on aluminum materials, they can stretch in terms of shape and size, assume their original form. This elastic and resilient feature makes them ideal for making various components, including masts and spars in sailboats.
-
Strength
Aluminum alloys come in a wide range of strengths, with some peaking at 300 MPa, exceeding that of some steel materials.
-
Lightweight
Aluminum weighs one-third of steel, iron, and other metals. Coupled with its resilience, strength, and other properties, most manufacturers use this engineering material as their first choice.
-
Resistance to Corrosion
Aluminum withstands the effects of weather elements protecting its surface with thin oxidized films. And even when there is a scratch, the affect surface layer quickly forms a coating to cover the affected part. Hence, manufacturers and engineers use this material in building, construction, and the production of household appliances.
-
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
As regarding the strength-to-weight ratio of a material, other metals pale in comparison to aluminum. Due to this unique quality, the element is a top material of choice in the aerospace industry and other fields.
Other qualities of aluminum include its capacity to conduct heat and electricity, its ductility under low temperatures, and its non-toxic, non-magnetic, non-sparking, and non-combustible features.
As a result of aluminum alloy characteristics, it also comes with several advantages for various industrial applications.
-
Physically Appealing
Aluminum alloys have aesthetic metallic surfaces that do not require additional finishing. Even if a machinist would want to add more protection to the surface layer, what the individual needs is to anodize the natural oxide film, which will increase its thickness without ruining the alloy surface.
-
Fabrication
Manufacturers can cut, draw, bend, and fabricate materials out of aluminum alloys quickly, including sheets, foils, rods, wires, and tubes. This feature is one of the prerequisites for machining metals in the CNC prototyping industry.
-
Integration
With aluminum alloys, engineers can join two or more parts together with ease using different methods, such as brazing, welding, riveting, soldering, clipping, bolting, adhesive bonding, and the rest. These materials can either be of aluminum properties or an entirely different composition.
Other advantages include reduced shipping and handling costs, vast finishes, seamless production, uniform quality, broader design capabilities, cost-effectiveness, and easy recycling.
Advantages of CNC Machining Aluminum Prototype
Since aluminum prototypes stem from aluminum alloys, the former shares the same properties and advantages with the latter. Here are some of the merits of manufacturing these prototypes using CNC technology.
-
Reduced Cost
CNC-machined aluminum components are less expensive than other metals like steel, due to the short time it takes to fabricate them. Besides, they do not need more surface finishes. Manufacturers only enhance its strength by adding small quantities of copper, magnesium, and zinc; the reason being that aluminum in its raw form is soft.
-
Clear-Cut Machining
With CNC technology, machinists can easily cut, punch, drill, and fold aluminum materials into any desired form and dimension. Besides, this methodology requires less energy when compared to other machining processes.
-
Malleability
Aluminum prototypes can easily bend to any degree during CNC machining, unlike its counterpart – steel. For this reason, CNC shops can incorporate various molding techniques to produce a wide variety of aluminum shapes.
-
Custom Finish
With CNC machining, manufacturers can customize aluminum prototypes based on an end user’s requirements (design and specification). This process includes adding custom colors, engravings, and additional components to give the product a custom look.
-
Resistance to Low Temperatures
When compared to steel, aluminum components perform excellently under low temperatures. It is easy to cut and weld each part of the metal to produce the desired outcome.
Surface Treatment for Aluminum Prototypes
In the CNC prototyping industry, manufacturers implement surface treatment in enhancing the aesthetics and functionality of machined products. This process makes the end product more appealing to clients and the market at large. Here are some standard surface treatments for aluminum prototypes:
-
Sand Blasting
Also known as shot peening, this procedure involves the use of sand flow at high speeds to clean and graze the surface of the aluminum component to cover up defects, produce a different degree of roughness, and enhance its appearance. This process also makes the material more adhesive to the coating. Machinists can use either the thin sand or the glass beads sand to produce varying effects on the metal.
-
Electroplating
There are two types of electroplating under aluminum surface treatments; they include vacuum plating and water plating. This process protects the aluminum component from corrosion by forming a protective layer of film on its surface. As a result, if there is an exposure to air, the material will remain intact.
-
Anodizing
This type of surface treatment is ideal for aluminum components that are to undergo dyeing. Anodizing improves the physical properties of an aluminum product, as well as protect it from etching. The material becomes more resistant to wear and tear, insusceptible to surface hardness, and has an extended service life. Above all, its improved aesthetics appeals to a wide range of customers.
-
Brushing
With this type of surface treatment, manufacturers can create a smooth texture that runs through the surface of an aluminum surface. This technique is useful in masking defects that may be present in a product while enhancing its aesthetics. However, to prevent corrosion, this treatment procedure is only effective after the material has undergone oxidation.
-
Polishing
There are various means of polishing an aluminum component surface; these include the use of mechanical polishing, electrolytic polishing, and chemical polishing. Using a combination of the first two surface treatment procedures, a machinist can create a bright, smooth texture on an aluminum surface, to the point that it has a mirror-like effect similar to that of stainless steel. This process gives the product a top-quality look and feel.
Common Issues in Machining Aluminum Prototypes
-
Deformity of the Alloy
Aluminum alloys come with individual tempers, which makes some easier to fabricate than others. Also, due to its softness at a pure state and its high thermal expansion, it is hard to machine the metal without increasing its hardness with other materials. In most cases, the material tends to deform when cutting and then fuses to the cutting edge of the CNC machining tool. For this reason, it is essential to select an alloy that has undergone tempering. Additionally, a precise machining technique is vital when fabricating an aluminum alloy, including the use of symmetrical machining and stratified multiple machining.
-
Poor Quality Material
In CNC-machined aluminum prototyping, high-grade materials determine the aesthetics and functionality of the end product. Inferior quality materials affect the manufacturing process of a prototype, as manufacturers have to deal with problems like defects resulting from inclusions and pitting during oxidization. Hence, to get the best result and enhance the development cycle of an aluminum component, CNC shops are to use superior materials.
-
Sub-par Machining Tools
Using a wrong tool can affect the machining process of an aluminum prototype as the component tends to stick excessively to the CNC tool when machining at incredible speeds, thereby creating build-ups that, in turn, dull the machining tool and slows down the process.
Summary
CNC aluminum machining is one of the highly effective processes in the CNC prototyping industry. Using this technology, manufacturers can produce aluminum components with excellent properties, repeatedly, with high precision and at incredible speeds. To further fabricate aluminum prototypes that offer higher performance, CNC shops can combine CNC machining with other methodologies, including aluminum extrusion, forging, die casting, and investment casting. There is a vast range of opportunities to explore with this technology.
This article does not necessarily reflect the opinions of the editors or management of EconoTimes



 Nasdaq Proposes Fast-Track Rule to Accelerate Index Inclusion for Major New Listings
Nasdaq Proposes Fast-Track Rule to Accelerate Index Inclusion for Major New Listings  Ford and Geely Explore Strategic Manufacturing Partnership in Europe
Ford and Geely Explore Strategic Manufacturing Partnership in Europe  Prudential Financial Reports Higher Q4 Profit on Strong Underwriting and Investment Gains
Prudential Financial Reports Higher Q4 Profit on Strong Underwriting and Investment Gains  CK Hutchison Launches Arbitration After Panama Court Revokes Canal Port Licences
CK Hutchison Launches Arbitration After Panama Court Revokes Canal Port Licences  Weight-Loss Drug Ads Take Over the Super Bowl as Pharma Embraces Direct-to-Consumer Marketing
Weight-Loss Drug Ads Take Over the Super Bowl as Pharma Embraces Direct-to-Consumer Marketing  Instagram Outage Disrupts Thousands of U.S. Users
Instagram Outage Disrupts Thousands of U.S. Users  Trump Backs Nexstar–Tegna Merger Amid Shifting U.S. Media Landscape
Trump Backs Nexstar–Tegna Merger Amid Shifting U.S. Media Landscape  Amazon Stock Rebounds After Earnings as $200B Capex Plan Sparks AI Spending Debate
Amazon Stock Rebounds After Earnings as $200B Capex Plan Sparks AI Spending Debate  Sony Q3 Profit Jumps on Gaming and Image Sensors, Full-Year Outlook Raised
Sony Q3 Profit Jumps on Gaming and Image Sensors, Full-Year Outlook Raised  Nvidia, ByteDance, and the U.S.-China AI Chip Standoff Over H200 Exports
Nvidia, ByteDance, and the U.S.-China AI Chip Standoff Over H200 Exports  Uber Ordered to Pay $8.5 Million in Bellwether Sexual Assault Lawsuit
Uber Ordered to Pay $8.5 Million in Bellwether Sexual Assault Lawsuit  TrumpRx Website Launches to Offer Discounted Prescription Drugs for Cash-Paying Americans
TrumpRx Website Launches to Offer Discounted Prescription Drugs for Cash-Paying Americans  Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang Says AI Investment Boom Is Just Beginning as NVDA Shares Surge
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang Says AI Investment Boom Is Just Beginning as NVDA Shares Surge  SpaceX Pushes for Early Stock Index Inclusion Ahead of Potential Record-Breaking IPO
SpaceX Pushes for Early Stock Index Inclusion Ahead of Potential Record-Breaking IPO  Tencent Shares Slide After WeChat Restricts YuanBao AI Promotional Links
Tencent Shares Slide After WeChat Restricts YuanBao AI Promotional Links  Rio Tinto Shares Hit Record High After Ending Glencore Merger Talks
Rio Tinto Shares Hit Record High After Ending Glencore Merger Talks  Once Upon a Farm Raises Nearly $198 Million in IPO, Valued at Over $724 Million
Once Upon a Farm Raises Nearly $198 Million in IPO, Valued at Over $724 Million